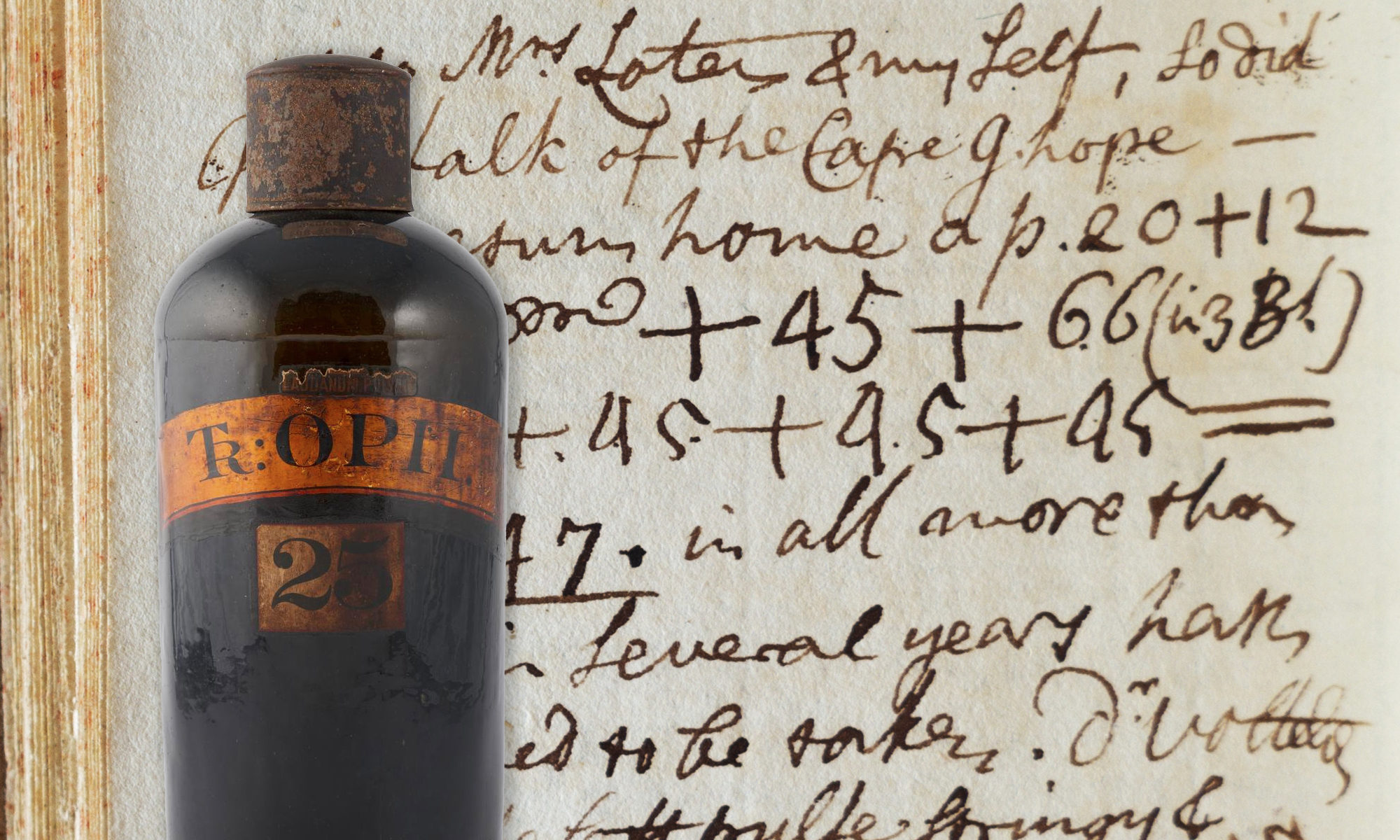The word ‘intoxicant’ has a central place in this project, as in wider scholarship. But what does the term really mean, and why do historians use it so regularly? Intoxicant is mainly used mainly to describe products which intoxicate – that ‘fuddle or make drunk’, or that artificially alter one’s physiological or neurological state. As Phil Withington and others have argued, whereas alternative words like ‘drugs’ possess strong ideological connotations pertaining to modern society and are more limited in what they evoke (mainly classified substances), intoxicant is a broadly encompassing neutral term, making it useful for describing and investigating a host of present-day consumables in different historical contexts. Usually, as in the Intoxicating Spaces project, scholars who talk about intoxicants refer to a familiar range of narcotics such as alcohols, coffee, opium, tea, and tobacco. Most of these commodities became popular from the early seventeenth century onwards as a consequence of increasing global trade and colonialism.
Worlds of Opiates Webinar
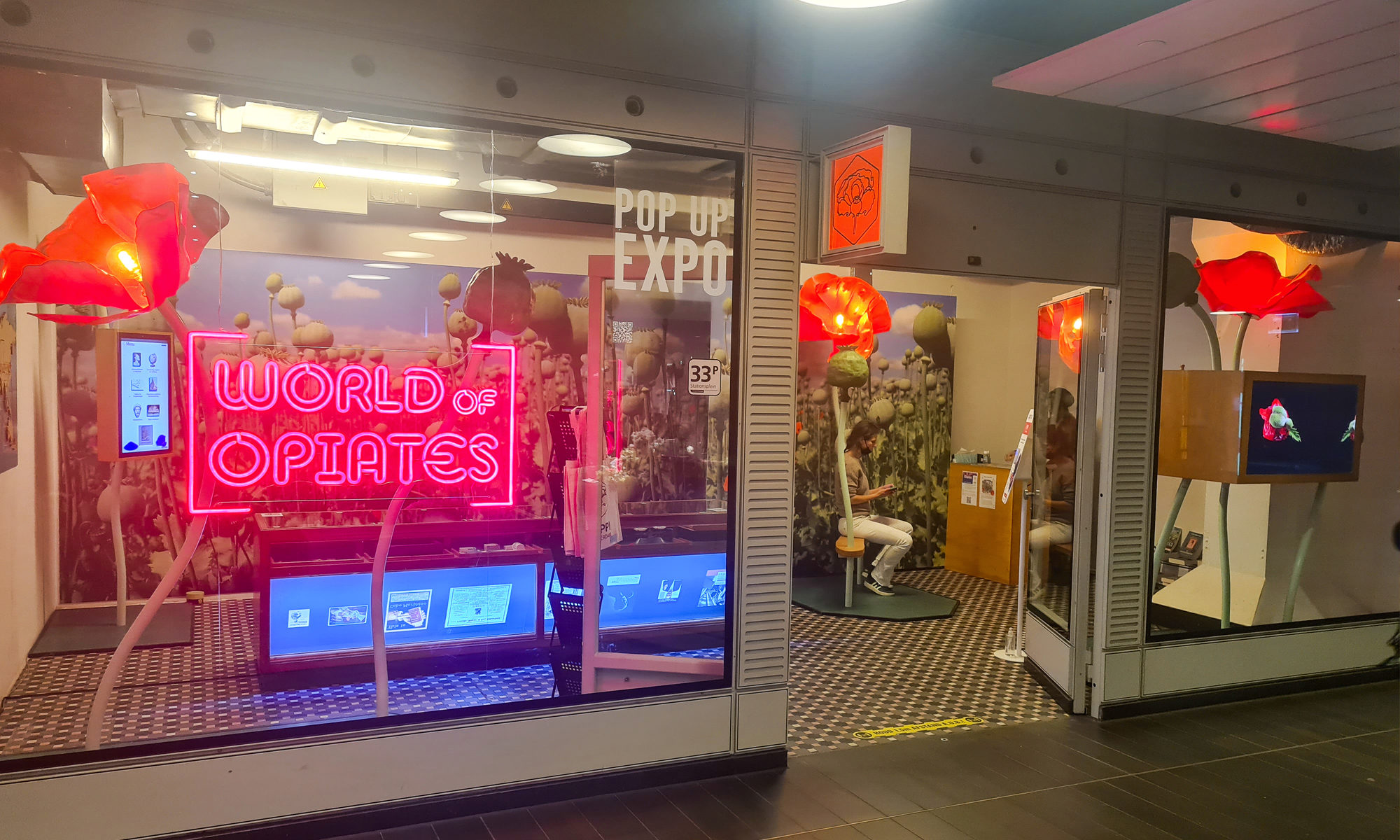
The project rounded out 2021 with a ‘big bang’ in Amsterdam, when work on opium by our Utrecht research team was translated into a unique project in public space: Worlds of Opiates, a pop-up exhibition co-created with artist Corne van der Stelt, Het Uitvindersgilde, and Poppi, a start-up drugs museum and social enterprise. Visitors to the show walk through an immersive field of giant 3D poppy flowers, and discover the many attributes of the most powerful flower known to mankind. Interactive elements tell stories about opium, laudanum, heroin, and painkillers, the same substance in different guises eliciting different societal responses.
New Project Exhibition: Worlds of Opiates
From 3 December 2021–29 March 2022, our Utrecht research team will hold a free pop-up exhibition for the general public at Amsterdam Central Station, one of the city’s major thoroughfares. The interactive show, organised in conjunction with the Poppi Drug Museum and called Worlds of Opiates, invites visitors to explore the history of opium in Amsterdam and its associated public spaces in a global context. Drawing on the findings of the project, and incorporating data from the 1970s and 1980s produced by our HERA partner project Governing the Narcotic City and the Mainline Foundation for harm reduction, the exhibition features both physical and digital objects, as well as historic maps of opium distribution in Amsterdam. Visitors can open and investigate the drawers of an original apothecaries’ counter, watch slideshows, access additional information on their mobile devices via QR codes, or listen to lectures by historians on topics such as opium use among the eighteenth-century Dutch elite, early modern opium use in Scotland, or the drug’s connection with Afghanistan.
Continue reading “New Project Exhibition: Worlds of Opiates”
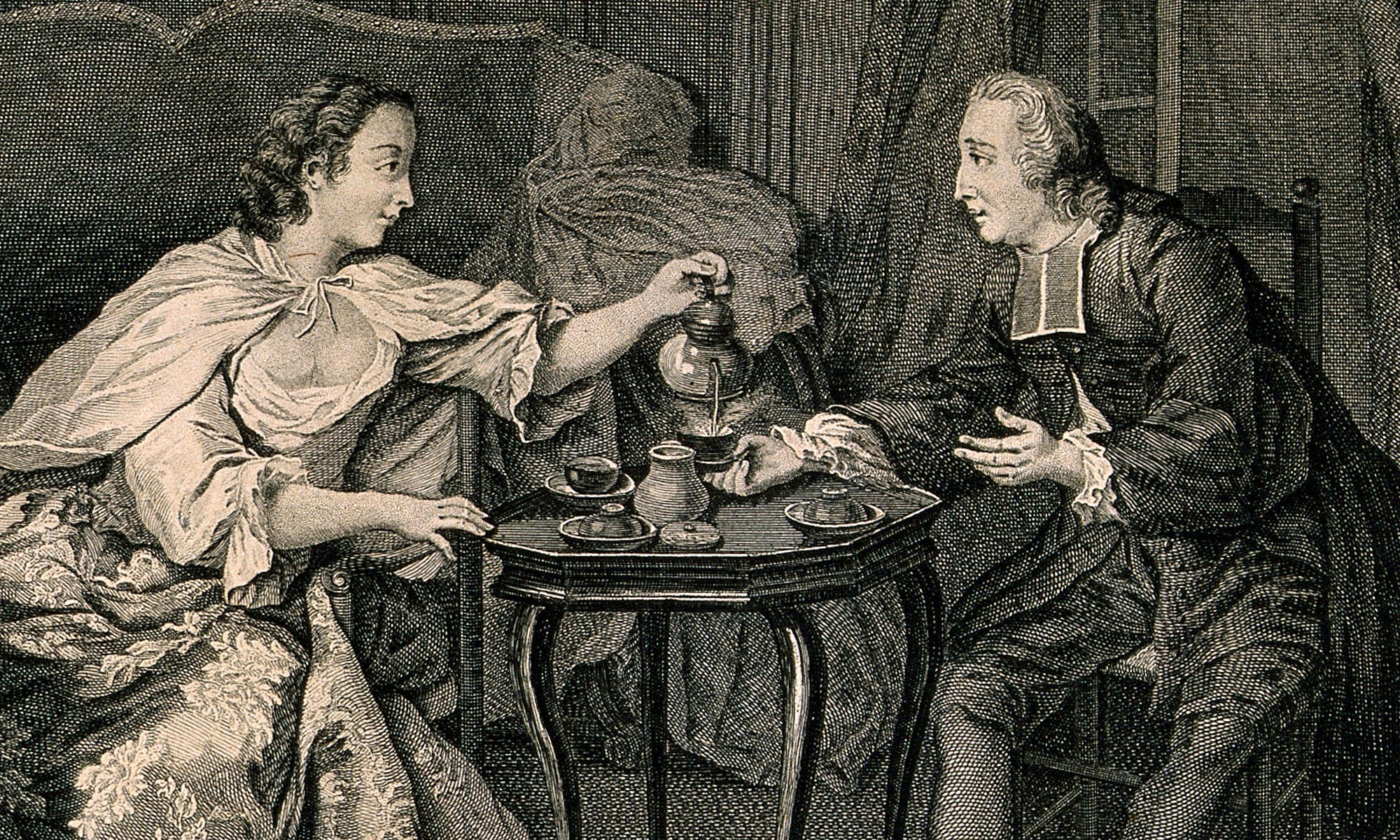
Loten’s Dagwyser (1783): A Notebook of a Reluctant Dutch Opium Eater
In Utrecht University Library there is a Dagwyser, or almanac, for the year 1783, which formerly belonged to Joan Gideon Loten (1710–1789), a Dutchman, who had been Governor of Makassar [Sulawesi, Indonesia] (1744–1749) and Ceylon [Sri Lanka] (1752–1757) and who spent most of his career with the Dutch East Indies Company. The Dagwyser is a booklet covered by green parchment, a so-called ‘envelope book’. The entries in the almanac were written in his house in Drift 27, Utrecht, today the location of the university library. The notebook contains short entries nearly every day, mostly in English and Dutch. It contains notations about the people he met in town, who he visited, or who visited him and his wife. A keen ornithologist, he also recorded bird sightings, and noted thoughts and questions to himself.
Continue reading “Loten’s Dagwyser (1783): A Notebook of a Reluctant Dutch Opium Eater”
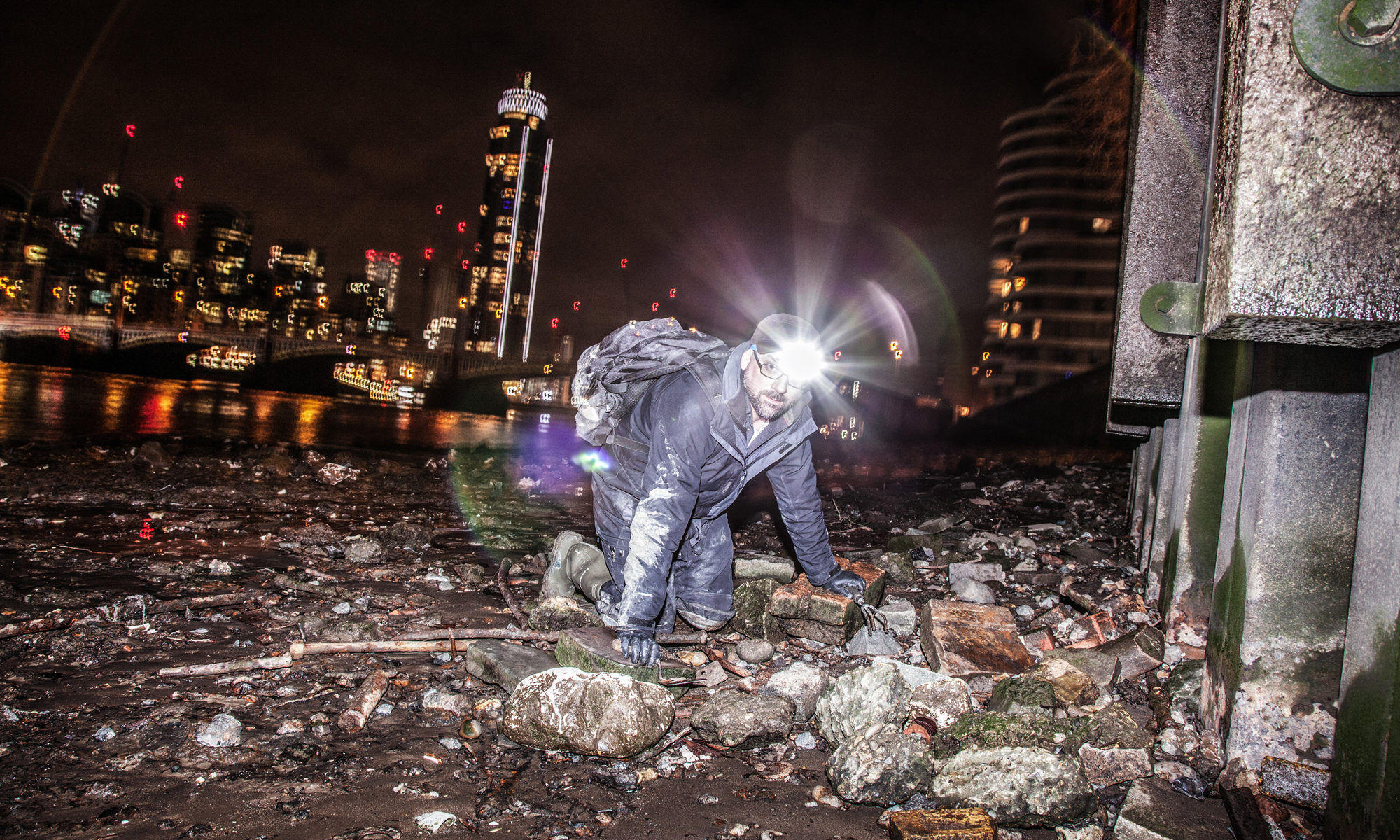
Exploring London’s Intoxicating Spaces Through Mudlarking
The River Thames as it flows through London is tidal, meaning twice per day part of the riverbed is exposed for a few hours. This area, known as the Thames foreshore, is a rich archive of (among other things) the remnants of two millennia of the city’s relationship with intoxicants. From tobacco to sugar to opium, the river delivers evidence of how they were imported, refined, sold, and consumed, but it is an archive like no other.
Continue reading “Exploring London’s Intoxicating Spaces Through Mudlarking”
Beer, Wine, and Spirits: Reflections on Intoxicants and Ghosts
This spooky season, while holed up in an isolated farmhouse in deepest North Yorkshire, I’ve been thinking about the connections between intoxicants and ghosts, which haven’t been fully explored in the extensive academic literatures around either topic, but which seem to be many and various.
Continue reading “Beer, Wine, and Spirits: Reflections on Intoxicants and Ghosts”
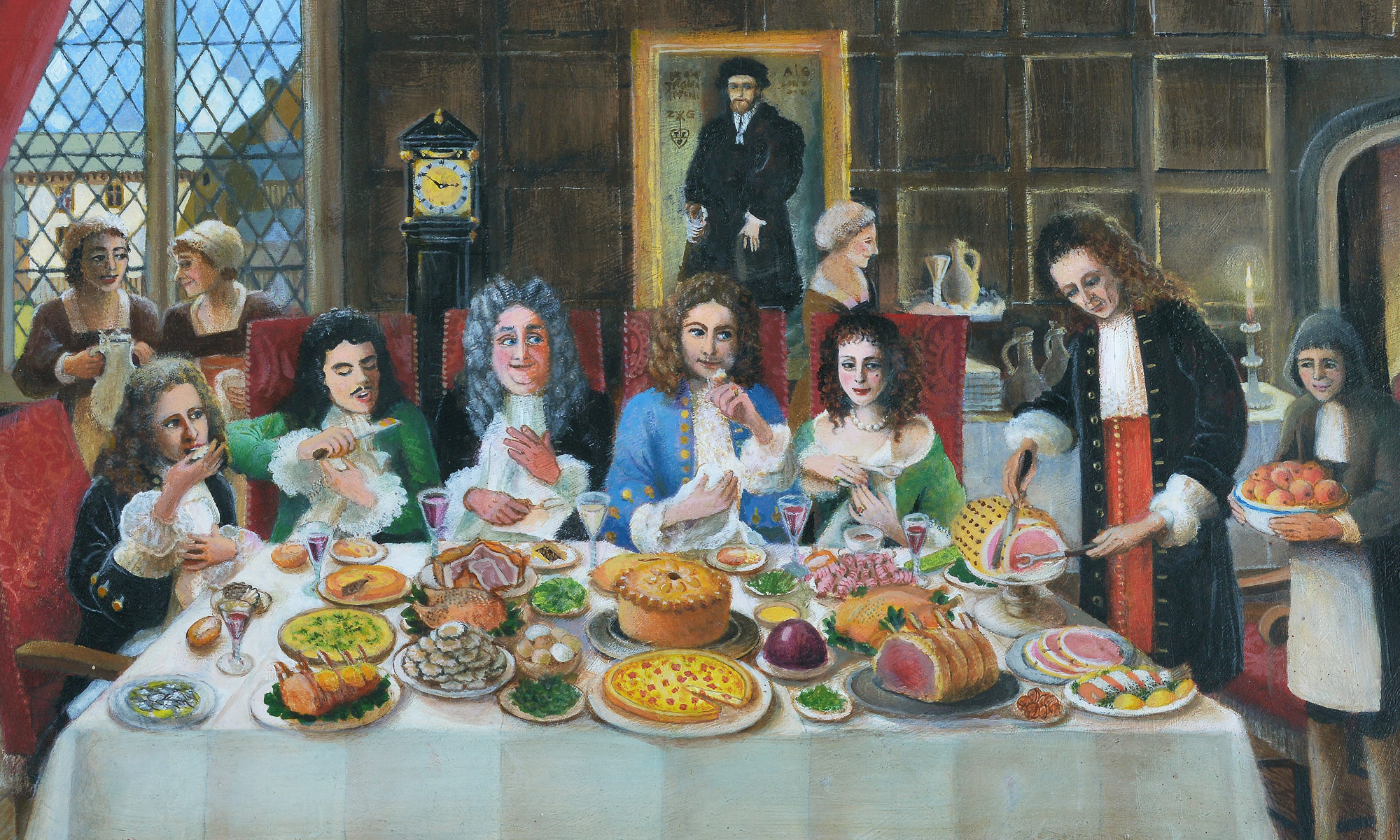
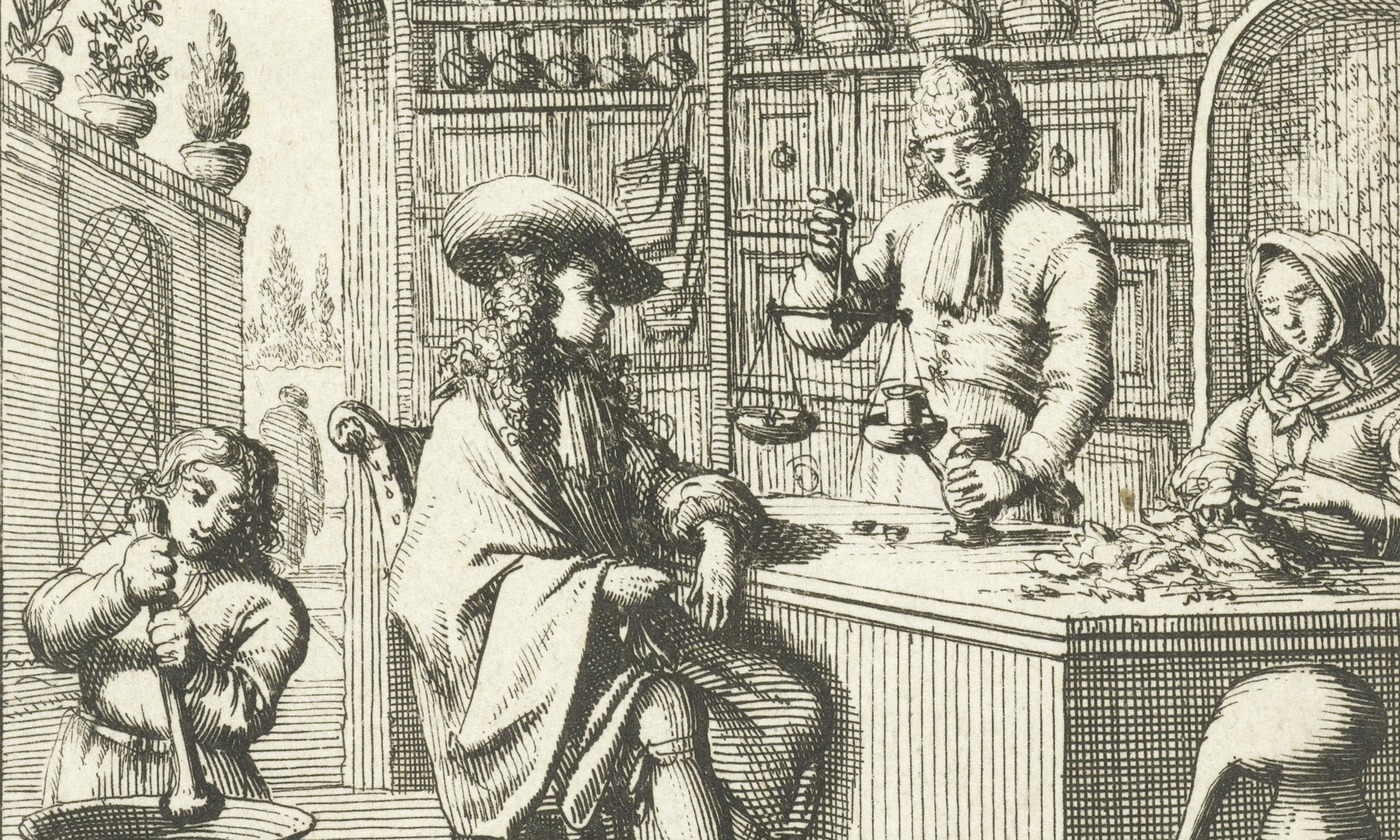
Intoxicating Pharmacies? Apothecary Shops and New Intoxicants in Amsterdam, 1600–1850
Thinking about intoxicating spaces, apothecary shops are probably not what first springs to mind. Yet, these places are very relevant in discussing the assimilation of new intoxicants into European diets. It may seem strange to us today, but they virtually all started out as medicinal drugs. For example, sugar was believed to remedy coughing and to support the stomach, kidneys, and bladder, amongst others. Similarly, tobacco could be applied for many different conditions ranging from scurvy and tetanus to epilepsy and constipation. Moreover, it could be applied to cure wounds and was believed to have a preventative effect against the plague. Opium, coffee, tea, and cocoa were used just the same as panaceas for many ailments. The opium poppy’s bulbs and their sap were famous for their ability to induce sleep and to calm children. Tea and chocolate would even arouse lust, while coffee was regarded as an anti-love elixir.